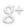| Name |
Application |
Machinability |
Weldability |
Corrosion Resistance |
| Aisi 304 |
| Excellent corrosion resistance property in annealed condition. Strength as well as hardness can be vary i.e increased or decreased substantially by cold working. |
|
Moderate machinability |
304 is readily wieldable by arc welding process , with air cooling gives good toughness property.. |
High corrosion resistance in general atmospheric corrosive environment, excellent resistance to most oxidising agent, sterilizing solution, dyestuff, most organic chemicals, inorganic chemical, hot petroleum gases, steam combustion gases, nitric acid. |
| Aisi 304L |
Better corrosion resistnce, high ductility, excellent drawing , forming and spinning |
It has machinability of about 40% of free machining mild steel. |
| The austenitic class of stainless steels is generally considered to wieldable by arc welding process , with air cooling gives good toughness property.
|
|
304L exhibit excellent resistance to a wide range of atmospheric, chemical, textile, petroleum and food industry exposures |
| Aisi 316 |
Good strength and excellent corrosion resistance in annealed condition. However strength and hardness can be increased substantially by cold working. Inclusion of molybdenum improves its creep resistance at elevated temperature. |
| More difficult to machine. 316 has machinability rating around half to the free machining mild steel. |
|
316 is readily wieldable by arc welding process , with air cooling gives good toughness property |
High corrosion resistance in marine and industrial atmosphere, excellent resistance to chloride attack and against complex sulphur compound. Inclusion of molybdenum increases its resistance to pitting corrosion. |
| Aisi 316L |
Good strength and excellent corrosion resistance in annealed condition. However strength and hardness can be increased substantially by cold working. Inclusion of molybdenum improves its creep resistance at elevated temperature. |
Slightly more difficult to machine. 316L has machinability rating around half to the free machining mild steel.. |
316L is readily weldable by arc welding process , with air cooling gives good toughness property |
High corrosion resistance in marine and industrial atmosphere, excellent resistance to chloride attack and against complex sulphur compound. Inclusion of molybdenum increases its resistance to pitting corrosion. It also displays good oxidation resistance at elevated temperature and resist crevice corrosion |
| Aisi 317 |
High strength and high corrosion resistance. Superior pitting resistance. |
As 317 has higher toughness, it is recommended to use chip breaker. Hardenability will be reduced if constant feed and low speed is used. |
317 is readily weldable by arc welding process , with air cooling gives good toughness property |
317 has Excellent resistance to oxidation, sulphuric acid and chloride attacks. Also resist crevice corrosion. |
| Aisi 317L |
High strength, high corrosion resistance and stronger welds due to lower carbon content. |
Low speeds and constant feeds will minimize this alloy’s tendency to work harden.
As it tougher it produces stringy chip, so chip breaker is needed during machining. |
It is readily wieldable by arc welding process , with air cooling gives good toughness property. 317L with low carbon content can be welded without sensitisation to intergranular corrosion resulting from chromium carbide precipitation resulting in grain boundaries. |
Excellent corrosion resistance in wide range of chemicals like tartaric sulphurous, formic and citric, especially in acidic chloride environment or halides. |
| Aisi 347 |
347 is a stabilized stainless steels which offer an excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion following exposure to temperatures in the chromium carbide precipitation |
Slow speeds and positive feeds will reduce the tendency of work harden to alloys. Machining will produces stringy chips shows tough to machining same as 316L. |
347 can be welded by all commonly used wieldable by arc welding process . |
347 offer similar resistance to general, overall corrosion as the unstabilized chromium nickel Type 304. It shows good resistance in high temperature applications where high resistance to sensitization is essential, thereby preventing intergranular corrosion at lower temperatures. |